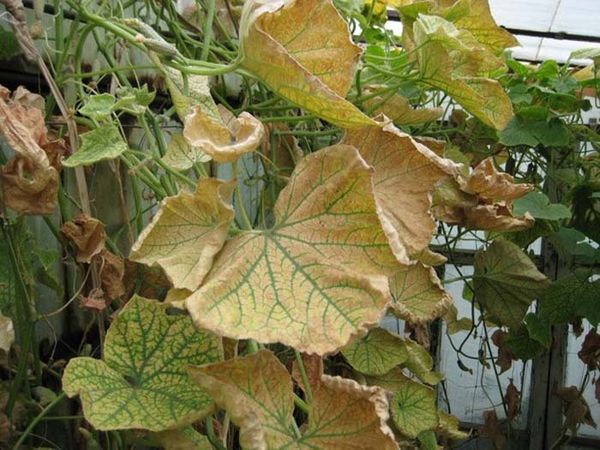
Cucumbers are well cultivated in almost all regions of our country. They are grown even on the windowsill. Fresh aroma and delicate flavor complements many dishes. However, not every gardener can boast of a generous harvest, there are many diseases that significantly reduce the fruiting plants. Armed with knowledge, it is quite possible to cope with any threats and diseases of cucumbers.
Table of contents
The most common diseases of cucumber in the greenhouse and open ground
This article focuses on the diseases of cucumbers. Having information about the signs of an infection, it is possible to react faster, thereby localizing the problem at the initial stage.
The fight against disease begins more from autumnwhen it comes time to prepare a bed for the next season. The quality of cleaning the soil from plant residues forms the basis of the future harvest.
In addition to compliance with the rules of agricultural technology is important regularly. inspect the plants, fixing any changes. As the leaves, inflorescences and fruits can be diagnosed and take immediate action to localize the affected area.
Brown olive spot (cladosporiosis)
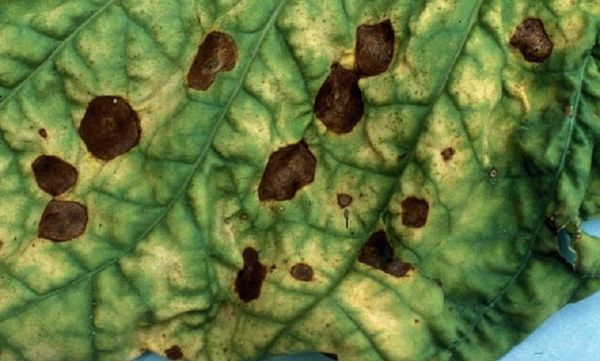
Fungal disease transmitted to healthy plants from plant debris or due to a sharp temperature drop. The development of the fungus is also noted from watering the beds with cold water using sprinkling.
The first signs can be found on the leaves and cuttings in the form brown oily spots. Later, spotting is covered and the fruit that penetrates the sores changes its dark color to a light color.
When transplanting seedlings of early varieties or growing crops from seeds should protect beds with film or other material for protection against low temperatures. If the climate features of the region are characterized by high humidity, it is recommended to choose varieties resistant to cladosporia.
For the prevention and localization of the affected area should be carried out for the season up to 4 treatments of cucumbers Bordeaux Blend (copper oxychloride).
Fusarium wilt

Symptoms: wilting the top of the bush and individual sheets. Also, decay of the root part of the stem is observed. The pathogen can be transmitted both through seed and the soil, so disinfection in this case is an integral part of prevention.
First aid is to control irrigation and control the temperature of the liquid used. In greenhouses need to improve the ventilation system.
Gray rot
Watery spots on the stem, leaves and even inflorescences signal gray mold. The name of the disease was due to the characteristic color of the plaque on the formed spots. The affected flower dies, so it is important to instantly localize the hearth, otherwise the crop will be under threat.
At the first signs it is recommended to treat the plants. soda solution (75 grams of soda in a bucket of water). The procedure is repeated every 3 days.

White rot
Recognized on white on sheets of green leaves. Later the foliage starts to ache, darkens and crumbles.
In the greenhouse, such a problem arises due to insufficient ventilation, on the open ground - due to thickening and neighboring weeds.
To stop the development of rot it is necessary to spray the beds copper sulphate solution (for 10 l of water take 2 g of vitriol and 10 g of urea).

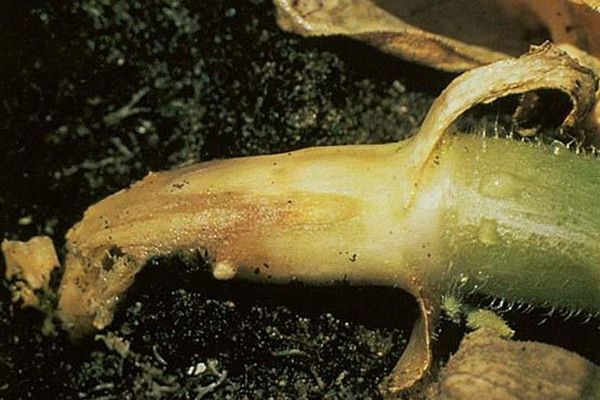
Root rot
The disease may be of fungal or bacterial origin. The reason for the defeat of cucumbers lies in the absence of disinfection of seeds and soil. To provoke the development of the disease can saline soil, a sharp temperature drop.At the roots, the process of reproduction of microorganisms continues even in dry soil, the main thing is that it should be warm.
Symptoms of root rot: wilting of leaves, darkening of the root, destruction of its structure (becomes rotten).
A drug Fitosporin-M used as a prophylactic treatment, and for the localization of the affected area.

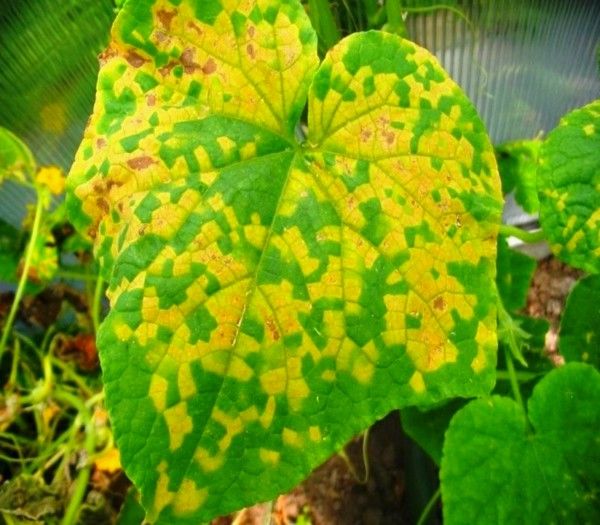
Field mosaic
Viral disease, often transmitted from weeds. Already on the seedlings can be found yellowing sheets twisting into a straw. Observed on the stem longitudinal cracking.
It is not worth planting infected shoots, there will be little sense from them, but healthy seedlings will be endangered.
In adult culture, mosaic is recognized by its characteristic stains on leaves and fruits. Flowers on infected bushes are not tied or showered.
When identifying the first signs, remove the affected plant fragments and spray the bed with drugs: Aktara, Aktellik.

Anthracnose
In place of the hearth are formed brown spotswhich increase in size and change color to darker (up to black). Over time, the spotting dries and disintegrates, with the result that the sheets become full of holes (as if burned).
Over time, green spots also form depressed spots, plunging into the pulp up to 5 mm. A common cause of plant contamination is seeds collected from infected fruits. Therefore, before planting, it is necessary to disinfect both the seed and the soil.
After the discovery of the disease need to treat the beds Bordeaux mixture, sulfur preparations or means "Kvadris".

Bacteriosis
The disease affects the cotyledons, leaves and fruits, forming on them watery spots. Over time, they become brown, the sheets dry out and crumble, the fruits become covered with sores.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to regularly spray young shoots with the preparation. Hom (on a bucket of water 40 g of funds), growth stimulator Energen (5 ml per 10 l of water).
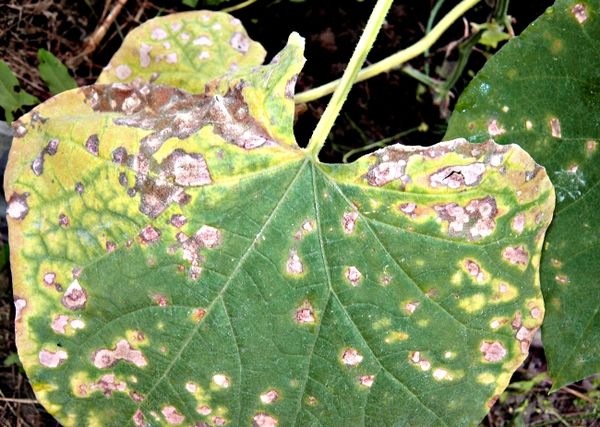

Protection of cucumbers from diseases
To reduce the risk of developing cucumber diseases, it is recommended to observe preventive measures. Among the main ones:
- compliance crop rotation;
- seed disinfection (soaking in a solution of potassium permanganate);
- soil disinfection (watering with boiling water, a solution of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate of low concentration);
- sorting seeds before sowing in order to select the healthiest and strongest;
- in the presence of outbreaks of fungal and viral diseases, it is necessary to replace the top layer of soil (especially important for greenhouses);
- timely weed removalwhich create a favorable environment for the development of harmful microorganisms;
- fertilization of the soil and the introduction of fertilizing according to the schedule will strengthen the culture immunity, make it immune to infections;
- at the end of the season, all plant debris is removed from the beds, it is in them that the larvae and fungal spores overwinter.

Prevention and treatment of folk remedies
Well proven popular recipes:
- An infusion of water (1 l) and wood ash (100 g.) Is left to stand for at least 2 days, after which it is supplemented with soap (4 g.) Rubbed on a small grater. It will take 2 treatments at weekly intervals.Effectively sprayed at the first signs of powdery mildew or as a preventative measure.
- Dry plants (nettle, tansy, wormwood) in a total weight of 100 grams. Pour 1 liter of boiling water and let it brew for about 2 hours. Strain the liquid with a sprinkling of cucumbers with an interval of 7-10 days with suspected powdery mildew.
- In case of downy mildew, it is recommended to sprinkle with a solution that consists of water (7 l), serum (3 l), vitriol (10 g).
- Scare away pests and relieve powdery mildew garlic tincture (30 g. Minced garlic is poured over 1 liter of water and lasts a day, after which another 9 l of water is added).
- In the fight against root rot use a tool that is prepared from the following ingredients: milk (1 l), iodine (30 drops), water (10 l), laundry soap (20 gr.).
- Dusting the soil with wood ash or lime will help disinfect the bed from harmful microorganisms. It is recommended to carry out the procedure 1 time in 10-14 days.
What kind of drugs spray for disease control
At intensive distribution diseases it is recommended to resort to more radical measures of treatment - the use of special drugs (fungicides).Handle and splash cucumbers with them is only clear according to the instructions.
Among the popular:
- Phytosporin;
- Kuprosat;
- Ridomil Gold;
- Aktara;
- Kvadris and others
There are a lot of dangers for cucumbers, but most of the problems can be prevented by preventive measures and timely care.
Experienced gardeners have developed many methods of controlling pests and infections, and willingly share the most effective recipes.
